Oneida Health
What is a Dobutamine Stress Echocardiogram
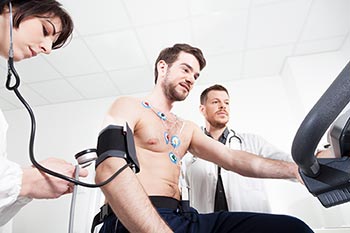 A Dobutamine Stress Echocardiogram or DSE is generally done if a patient is unable to exercise on a treadmill to stress the heart, like in a typical stress test. A medication called dobutamine is administered intravenously and causes the heart to beat more rapidly, mimicking the effect of exercise on the heart. Once dobutamine has been administered, the doctor will perform the echocardiogram.
A Dobutamine Stress Echocardiogram or DSE is generally done if a patient is unable to exercise on a treadmill to stress the heart, like in a typical stress test. A medication called dobutamine is administered intravenously and causes the heart to beat more rapidly, mimicking the effect of exercise on the heart. Once dobutamine has been administered, the doctor will perform the echocardiogram.
How the Test is Performed
As in a typical echocardiogram, electrodes are stuck onto your chest to record your heart rate and rhythm. An instrument called a transducer (similar to a microphone) that releases high-frequency sound waves is placed on your ribs and directed toward the heart. Other images will be taken from other locations on your chest. An echocardiogram allows doctors to see the heart beating, the heart valves, and other structures of the heart.
Why the Test is Performed
Doctors may want to perform a DSE for the following reasons:
- To assess the heart’s function and structure
- To further assess known heart valve disease
- To determine safe limits of exercise or activity after a heart attack, heart surgery, or other cardiac issue
- To evaluate cardiac function prior to heart surgery
How to Prepare for the Test
- Tell the doctor if you are allergic to latex or any medications.
- You may be asked to fast (not eat) prior to the test. You will be given instructions about when to stop eating or drinking prior to the test.
- Tobacco products and caffeinated beverages may be restricted several hours prior to the test.
- Tell the doctor about all medications you are taking including supplements and herbs.
- You may be asked to stop certain medications before the test, such as beta-blockers.
- Tell the doctor if you are pregnant or could be pregnant.
- Tell your doctor if you have a pacemaker.
- Depending on your medical condition, your doctor may make additional preparations.
What to Expect During the Test
A DSE may be done on an outpatient basis or you may have one done if you are staying in the hospital for a cardiac issue.
- You will remove any jewelry or other objects that may interfere with the test. You may wear glasses, dentures, or hearing aids.
- You will be given a gown to wear and be asked to remove clothing from the waist up.
- You will be asked to empty your bladder.
- An intravenous line (IV) will be started in your hand or arm to administer the dobutamine and give you fluids, if needed.
- You will start lying down on your left side on the table or bed, but you may be asked to change position during the test.
- Small electrodes will be placed on your skin which are connected to an electrocardiogram (ECG) monitor. The ECG will monitor and record your heart’s electrical activity.
- Your heart rate, blood pressure, breathing rate, and oxygen level will be monitored.
- The room will be dark so the technician can more easily view the images on the echo monitor.
- The technician will place warm gel on your chest and then position the transducer on the gel. You may feel a slight pressure as the technician moves the transducer to get the best image.
- The dobutamine infusion will be administered at a rate determined by your weight. The rate of the infusion will increase until you have reached your target heart rate, (determined by your doctor based on age and physical condition) or the maximum allowable dosage of dobutamine.
- After the dobutamine has been injected, your blood pressure will be checked, an ECG tracing will be conducted, and the echocardiogram images will be recorded. This process will be repeated after each increase in dobutamine.
- The dobutamine will be stopped after the target heart rate has been reached or the maximum amount has been administered. Your heart rate, blood pressure, and ECG will continue to be monitored for 10 to 15 minutes. Echocardiogram images will be recorded for a final time.
- Tell the technician if you feel chest pain, trouble breathing, sweating, or heart palpitations.
- Once the test has concluded and all images have been recorded, the gel will be wiped off, electrodes removed, and IV taken out of your hand or arm. You may then get dressed.
Potential Risks of the Test
There may be some risks associated with a DSE, including:
- Chest pain
- Severely high blood pressure
- Irregular heartbeats
- Dizziness
- Nausea
- Extreme tiredness
- Heart attack (rare)
Certain conditions may interfere with a DSE, such as:
- Smoking or using tobacco in any form within three hours of the test
- Ingesting caffeine within three hours of the test
- Taking beta-blocking medicines, as these make it hard to increase the heart rate